What is a Sacroiliac Joint Dysfunction?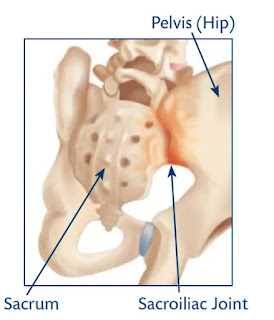
Sacroiliac Joint Dysfunction
Sacroiliac joint dysfunction refers to a condition in which there is a problem with the sacroiliac joint, which is located in the pelvis. The sacroiliac joint connects the sacrum, which is the triangular bone at the base of the spine, to the ilium, which is one of the bones that make up the pelvis.
The sacroiliac joint is responsible for transmitting the weight of the upper body to the lower body during activities such as walking, running, and jumping. When this joint is not functioning properly, it can lead to pain, discomfort, and limited mobility.
The causes of sacroiliac joint dysfunction can include trauma, pregnancy, arthritis, or degenerative changes in the joint.
Symptoms can include pain in the lower back, hips, buttocks, or legs, as well as stiffness or a feeling of instability in the pelvic region.
Treatment for sacroiliac joint dysfunction can include physical therapy, medication, and in some cases, surgery. A medical professional can help diagnose the condition and develop a treatment plan based on the individual's specific needs.
Related Anatomy
The sacroiliac joint is located between the sacrum and the ilium bones of the pelvis. The sacrum is a triangular-shaped bone located at the base of the spine, formed by the fusion of five vertebrae. The ilium is one of three bones that make up the pelvis, along with the ischium and the pubis.
The sacrum articulates with the ilium on each side of the body, forming the left and right sacroiliac joints. These joints are held together by strong ligaments that provide stability and support to the pelvis.
The sacroiliac joint is an important part of the musculoskeletal system as it helps to transfer weight and force between the upper body and the legs during movement. Dysfunction of this joint can lead to pain, discomfort, and limited mobility, as mentioned earlier.
Other important structures in the area include the gluteal muscles, which attach to the ilium and help to support the pelvis, and the sciatic nerve, which runs through the area and can be affected by dysfunction of the sacroiliac joint.
Causes of Sacroiliac Joint Dysfunction
Sacroiliac joint dysfunction can be caused by various factors, including:
Trauma: A fall, motor vehicle accident, or any other physical impact can cause injury to the sacroiliac joint.
Pregnancy: During pregnancy, hormones are released that can cause the ligaments surrounding the sacroiliac joint to become more relaxed, which can lead to instability and pain.
Arthritis: Inflammation in the sacroiliac joint caused by arthritis can lead to pain and discomfort.
Degenerative changes: Over time, the cartilage in the sacroiliac joint can wear down, leading to pain and dysfunction.
Leg length discrepancy: A difference in leg length can cause an uneven distribution of weight in the sacroiliac joint, leading to dysfunction and pain.
Poor posture: Poor posture can put excess strain on the sacroiliac joint and contribute to dysfunction.
Overuse: Repetitive activities such as running or lifting heavy objects can cause strain on the sacroiliac joint, leading to dysfunction over time.
It's important to note that sometimes the exact cause of sacroiliac joint dysfunction is unknown, and it may be a combination of factors that contribute to the condition. A medical professional can help diagnose the condition and develop a treatment plan based on the individual's specific needs.
Symptoms of Sacroiliac Joint Dysfunction
The symptoms of sacroiliac joint dysfunction can vary from person to person, but some common signs and symptoms include:
Pain: Pain in the lower back, buttocks, hips, or legs is a common symptom of sacroiliac joint dysfunction. The pain can range from a dull ache to sharp, stabbing pain and may be felt on one or both sides of the body.
Stiffness: Stiffness in the lower back or pelvic area can be a symptom of sacroiliac joint dysfunction, making it difficult to move or change positions.
Instability: A feeling of instability or weakness in the pelvis or lower back can be a sign of sacroiliac joint dysfunction.
Numbness or tingling: Numbness or tingling in the legs or buttocks can occur in some cases of sacroiliac joint dysfunction.
Clicking or popping: A clicking or popping sound may be heard or felt when moving the pelvis in some cases of sacroiliac joint dysfunction.
Pain when sitting or standing for prolonged periods: Prolonged sitting or standing can exacerbate the symptoms of sacroiliac joint dysfunction.
It's important to note that the symptoms of sacroiliac joint dysfunction can be similar to those of other conditions, so it's essential to see a medical professional for an accurate diagnosis.
Risk factor
There are several risk factors that can increase the likelihood of developing sacroiliac joint dysfunction, including:
Age: As people age, the cartilage in the sacroiliac joint can wear down, increasing the risk of dysfunction and pain.
Pregnancy: During pregnancy, the body produces hormones that can cause the ligaments surrounding the sacroiliac joint to become more relaxed, leading to instability and pain.
Previous injury: A history of trauma or injury to the sacroiliac joint can increase the risk of developing dysfunction in the future.
Arthritis: Inflammatory conditions such as arthritis can increase the risk of developing sacroiliac joint dysfunction.
Repetitive activities: Repetitive activities such as running or lifting heavy objects can put stress on the sacroiliac joint and increase the risk of dysfunction.
Poor posture: Poor posture can put excess strain on the sacroiliac joint, increasing the risk of dysfunction over time.
Leg length discrepancy: A difference in leg length can cause an uneven distribution of weight in the sacroiliac joint, increasing the risk of dysfunction.
It's important to note that while these risk factors can increase the likelihood of developing sacroiliac joint dysfunction, not everyone who has these risk factors will necessarily develop the condition. A medical professional can help diagnose the condition and develop a treatment plan based on the individual's specific needs.
Differential Diagnosis
The symptoms of sacroiliac joint dysfunction can be similar to those of other conditions, so it's important to consider a range of differential diagnoses. Some conditions that may need to be ruled out include:
Lumbar spinal stenosis: A condition in which the spinal canal narrows and puts pressure on the nerves in the lower back, causing pain and discomfort.
Herniated disc: A condition in which the cushioning discs between the vertebrae in the spine become damaged, leading to pain and discomfort.
Piriformis syndrome: A condition in which the piriformis muscle in the buttocks becomes inflamed and puts pressure on the sciatic nerve, causing pain and discomfort.
Osteoarthritis: A degenerative joint disease that can cause pain and stiffness in the joints, including the sacroiliac joint.
Rheumatoid arthritis: An inflammatory condition that can affect the joints, including the sacroiliac joint, causing pain and discomfort.
Infection: In rare cases, an infection in the sacroiliac joint or surrounding tissues can cause pain and discomfort.
Cancer: Although rare, cancer can spread to the sacroiliac joint or surrounding tissues and cause pain and discomfort.
It's important to note that a medical professional will need to perform a thorough examination and review of medical history to determine an accurate diagnosis and develop a treatment plan based on the individual's specific needs.
Complications
If left untreated, sacroiliac joint dysfunction can lead to a range of complications, including:
Chronic pain: Over time, sacroiliac joint dysfunction can lead to chronic pain that can interfere with daily activities and quality of life.
Sciatica: In some cases, sacroiliac joint dysfunction can cause compression or irritation of the sciatic nerve, leading to pain and discomfort in the lower back, buttocks, and legs.
Scoliosis: In rare cases, sacroiliac joint dysfunction can cause scoliosis, a condition in which the spine curves to the side, leading to a range of symptoms and complications.
Reduced mobility: The pain and discomfort associated with sacroiliac joint dysfunction can lead to reduced mobility and difficulty performing daily activities.
Depression and anxiety: Chronic pain can take a toll on mental health, leading to symptoms of depression and anxiety.
It's important to seek medical attention if you are experiencing symptoms of sacroiliac joint dysfunction to prevent the development of complications and improve the overall prognosis. With appropriate treatment, most individuals with sacroiliac joint dysfunction can experience relief from their symptoms and return to their normal activities.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of sacroiliac joint dysfunction typically involves a combination of a thorough medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests. Here are some common methods used to diagnose sacroiliac joint dysfunction:
Medical history: A doctor will review the patient's medical history, including any prior injuries or conditions that could be contributing to their current symptoms.
Physical examination: A physical examination will typically involve assessing the range of motion in the hips, back, and legs, as well as pressing on certain areas to identify areas of tenderness or pain.
Diagnostic injections: A diagnostic injection of numbing medication into the sacroiliac joint can help to confirm the diagnosis by temporarily relieving pain in the joint.
Imaging tests: X-rays, CT scans, or MRI scans may be used to assess the sacroiliac joint and surrounding structures and rule out other conditions that may be causing symptoms.
Provocative tests: These tests involve applying pressure or performing certain movements to the sacroiliac joint to see if they reproduce the patient's symptoms.
Blood tests: Blood tests may be used to rule out underlying conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis.
It's important to note that the diagnosis of sacroiliac joint dysfunction can be challenging and may require a combination of diagnostic methods to achieve an accurate diagnosis. A medical professional can help determine the best course of action based on the individual's specific needs.
Treatment of Sacroiliac Joint Dysfunction
The treatment of sacroiliac joint dysfunction typically involves a combination of conservative and more invasive interventions, depending on the severity of symptoms and the underlying cause of the condition. Here are some common methods used to treat sacroiliac joint dysfunction:
Rest and activity modification: Resting the affected area and avoiding activities that aggravate symptoms can help to reduce pain and inflammation.
Medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), muscle relaxants, and pain relievers may be prescribed to help manage pain and inflammation.
Physical therapy: A physical therapist can develop an individualized exercise program to help improve mobility, strength, and flexibility and reduce pain.
Chiropractic care: Chiropractors can use manual manipulation techniques to help realign the sacroiliac joint and reduce pain and discomfort.
Prolotherapy: A type of injection therapy that involves injecting a solution into the joint to help promote healing and reduce pain.
Radiofrequency ablation: A procedure in which a small electrode is inserted into the sacroiliac joint and radio waves are used to heat and destroy the nerves that are transmitting pain signals.
Surgery: In rare cases, surgery may be recommended to fuse the joint or to remove damaged tissue.
The choice of treatment will depend on the individual's specific needs, severity of symptoms, and underlying cause of the condition. It's important to work with a medical professional to develop a comprehensive treatment plan that can help improve symptoms and quality of life.
Physiotherapy treatment
Physiotherapy can be an effective treatment for sacroiliac joint dysfunction, with the goals of reducing pain, improving mobility, and restoring function. Here are some common physiotherapy treatments used for sacroiliac joint dysfunction:
Manual therapy: A physiotherapist may use manual therapy techniques such as mobilization or manipulation to improve joint mobility and reduce pain.
Stretching and strengthening exercises: A physiotherapist can develop a customized exercise program to help improve flexibility and strengthen the muscles around the sacroiliac joint.
Postural education: A physiotherapist can provide guidance on proper posture and body mechanics to help reduce stress on the sacroiliac joint and improve overall function.
Modalities: Modalities such as ice or heat therapy, ultrasound, or electrical stimulation may be used to help reduce pain and inflammation.
Core stabilization exercises: Strengthening the muscles of the core can help to support the lower back and pelvis, reducing stress on the sacroiliac joint.
Education: A physiotherapist can educate the patient on lifestyle modifications, such as avoiding certain activities or using proper body mechanics, to prevent further injury and improve symptoms.
It's important to work with a qualified physiotherapist who can develop an individualized treatment plan based on the patient's specific needs and goals. With appropriate physiotherapy treatment, many individuals with sacroiliac joint dysfunction can experience significant improvement in their symptoms and quality of life.
Exercise for Sacroiliac Joint Dysfunction
Exercise can be an effective treatment for sacroiliac joint dysfunction, with the goals of reducing pain, improving mobility, and strengthening the muscles around the joint. Here are some common exercises that may be recommended for individuals with sacroiliac joint dysfunction:
Pelvic tilts: Lie on your back with your knees bent and feet flat on the floor. Tighten your abdominal muscles and gently tilt your pelvis forward and backward, holding each position for a few seconds.
Gluteal sets: Lie on your back with your knees bent and feet flat on the floor. Squeeze your buttock muscles and hold for a few seconds before relaxing.
Bridging: Lie on your back with your knees bent and feet flat on the floor. Lift your hips off the ground, engaging your glutes and hamstrings, and hold for a few seconds before lowering back down.
Side-lying leg lifts: Lie on your side with your legs straight. Lift your top leg up and hold for a few seconds before lowering back down.
Clamshells: Lie on your side with your knees bent and feet together. Keeping your feet together, lift your top knee up and hold for a few seconds before lowering back down.
Cat-cow stretch: Start on your hands and knees with your hands directly under your shoulders and your knees directly under your hips. Arch your back and lift your head up to stretch your lower back, then lower your head and round your spine.
It's important to work with a qualified physiotherapist or exercise professional who can develop an individualized exercise program based on the patient's specific needs and goals. With appropriate exercise and strengthening, many individuals with sacroiliac joint dysfunction can experience significant improvement in their symptoms and quality of life.
How to Prevent Sacroiliac Joint Dysfunction?
There are several steps individuals can take to help prevent sacroiliac joint dysfunction:
Maintain good posture: Proper posture can help reduce stress on the sacroiliac joint. This includes sitting and standing with your shoulders back, chin tucked in, and your hips and knees at 90-degree angles.
Exercise regularly: Regular exercise can help strengthen the muscles around the sacroiliac joint and improve flexibility, reducing the risk of injury.
Use proper body mechanics: When lifting or carrying heavy objects, use proper body mechanics to avoid putting stress on the sacroiliac joint. This includes lifting with your legs instead of your back and keeping the object close to your body.
Wear supportive shoes: Wearing supportive shoes with good arch support can help reduce stress on the sacroiliac joint and prevent injuries.
Maintain a healthy weight: Being overweight can put extra stress on the joints, including the sacroiliac joint. Maintaining a healthy weight can help reduce the risk of joint problems.
Avoid high-impact activities: High-impact activities such as running or jumping can put stress on the sacroiliac joint and increase the risk of injury. If you engage in these activities, be sure to use proper technique and wear appropriate footwear.
It's important to listen to your body and seek medical attention if you experience any pain or discomfort in the lower back or pelvic region. By taking these preventative steps, individuals can reduce their risk of developing sacroiliac joint dysfunction and improve their overall joint health.
No comments:
Post a Comment